Web3 New Tale of Two Cities: Stablecoins and Money Market Funds
Original Article Title: Stablecoins and the parallels with Money Market Funds
Original Article Authors: @shawnwlim, @artichokecap Founders
Original Article Translation: zhouzhou, BlockBeats
Editor's Note: The regulatory dispute over stablecoins bears resemblance to the experience of Money Market Funds (MMFs) half a century ago. MMFs were initially designed for corporate cash management but faced criticism due to lack of deposit insurance and vulnerability to runs, impacting bank stability and monetary policy. Nevertheless, MMF assets now exceed $7.2 trillion. The 2008 financial crisis led to the collapse of the Reserve Fund, and in 2023, the SEC is still pushing for MMF regulatory reform. The history of MMFs suggests that stablecoins may face similar regulatory challenges but could ultimately become a crucial part of the financial system.
The following is the original content (slightly edited for readability):
Stablecoins are exciting, and the upcoming stablecoin legislation in the US represents a rare opportunity to upgrade the existing financial system. Those studying financial history will notice parallels between it and the invention and development of Money Market Funds about half a century ago.
Money Market Funds were invented in the 1970s as a cash management solution, primarily for corporates. At that time, US banks were prohibited from paying interest on balances in checking accounts, and corporations were often unable to maintain savings accounts. If a business wanted to earn interest on idle cash, they had to buy US Treasuries, engage in repurchase agreements, invest in commercial paper, or certificates of deposit. Managing cash was a cumbersome and operationally intensive process.
The design of Money Market Funds was to maintain a stable share value, with each share pegged at $1. The Reserve Fund, Inc. was the first MMF. Launched in 1971, it was introduced as "a convenient alternative for investing temporary cash balances," which would typically be placed in money market instruments like Treasuries, commercial paper, bank acceptances, or CDs, with an initial asset size of $1 million.
Other investment giants quickly followed suit: Dreyfus (now part of BNYglobal), Fidelity, Vanguard_Group. In the 1980s, almost half of Vanguard's legendary mutual fund business growth was attributable to its Money Market Fund.

During his tenure as Chairman of the Federal Reserve from 1979 to 1987, Paul Volcker was highly critical of Money Market Funds (MMFs). He continued his criticism of MMFs as late as 2011.
Today, many of the criticisms raised by policymakers against stablecoins echo those from half a century ago against Money Market Funds:
· Systemic Risk and Banking Safety Concerns: MMFs lack deposit insurance and a lender of last resort mechanism, unlike insured banks. Because of this, MMFs are susceptible to rapid runs, which could exacerbate financial instability and lead to contagion. There are also concerns that deposits shifting from insured banks to MMFs could weaken the banking sector as banks lose their low-cost and stable deposit base.
· Unfair Regulatory Arbitrage: MMFs provide bank-like services, maintaining a stable $1 share price, but without rigorous regulatory oversight or capital requirements.
· Weakening of Monetary Policy Transmission Mechanism: MMFs could weaken the Fed's monetary policy tools, as traditional monetary policy instruments like bank reserves are less effective when funds flow from banks to MMFs.
Today, MMFs have financial assets exceeding $7.2 trillion. For reference, M2 (excluding MMF assets) is $21.7 trillion.
In the late 1990s, the rapid growth in MMF assets was a result of financial deregulation (the Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act repealed the Glass-Steagall Act, fueling a wave of financial innovation), while the prosperity of the internet facilitated better electronic and online trading systems, speeding up fund inflows into MMFs.

Do you see a pattern here? (I would like to point out that even half a century later, the regulatory struggle around MMFs is far from over. The SEC adopted MMF reforms in 2023, including raising minimum liquidity requirements and removing fund manager restrictions on investor redemptions.)
Unfortunately, the Reserve Fund met its end after the 2008 financial crisis. It held some Lehman Brothers debt securities, which were written down to zero, leading to the fund's breaking of the buck event and significant redemptions.
Bạn cũng có thể thích
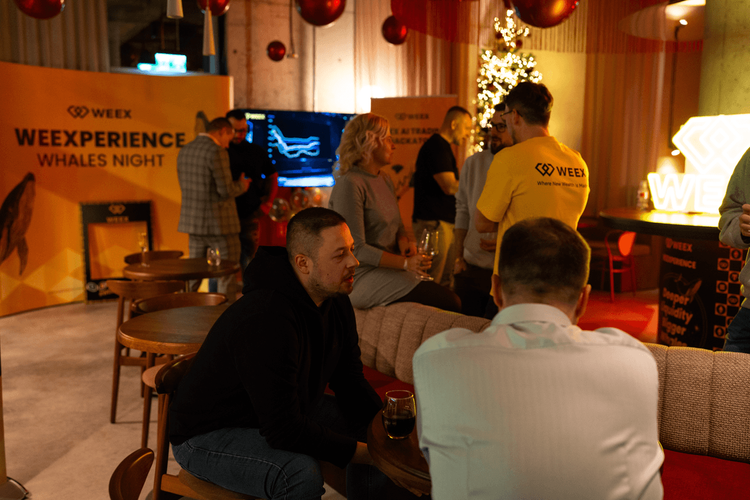

WEEXPERIENCE Whales Night: AI Trading, Crypto Community & Crypto Market Insights
Vào ngày 12 tháng 12 năm 2025, WEEX đã tổ chức WEEXPERIENCE Whales Night, một cuộc họp cộng đồng ngoại tuyến được thiết kế để tập hợp các thành viên cộng đồng cryptocurrency địa phương. Sự kiện kết hợp chia sẻ nội dung, trò chơi tương tác và bản trình bày dự án để tạo ra trải nghiệm ngoại tuyến thoải mái nhưng hấp dẫn.

Rủi ro giao dịch AI trong tiền mã hóa: Tại sao các chiến lược giao dịch tiền mã hóa tốt hơn có thể tạo ra tổn thất lớn hơn?
Rủi ro không còn nằm chủ yếu trong việc đưa ra quyết định kém hoặc sai lầm về cảm xúc. Nó ngày càng sống trong cấu trúc thị trường, con đường thực thi, và hành vi tập thể. Hiểu được sự thay đổi này quan trọng hơn là tìm ra chiến lược “tốt hơn” tiếp theo.

Các đại lý AI đang thay thế Nghiên cứu Crypto? Làm thế nào AI tự trị đang định hình lại giao dịch crypto
AI đang chuyển từ việc hỗ trợ các nhà giao dịch sang tự động hóa toàn bộ quá trình nghiên cứu đến thi hành trong thị trường tiền điện tử. Lợi thế đã chuyển từ kiến thức của con người sang đường ống dẫn dữ liệu, tốc độ và các hệ thống AI sẵn sàng để thực hiện, làm cho sự chậm trễ trong tích hợp AI trở thành một nhược điểm cạnh tranh.

Bot giao dịch AI và Giao dịch sao chép: Cách các chiến lược đồng bộ hóa định hình lại sự biến động của thị trường crypto
Các nhà giao dịch crypto bán lẻ từ lâu đã phải đối mặt với những thách thức tương tự: quản lý rủi ro kém, đăng ký muộn, quyết định về cảm xúc và thực thi không nhất quán. Các công cụ giao dịch AI hứa hẹn một giải pháp. Ngày nay, các hệ thống giao dịch sao chép và robot breakout được hỗ trợ bởi AI giúp các nhà giao dịch kích thước vị trí, đặt điểm dừng và hành động nhanh hơn bao giờ hết. Ngoài tốc độ và độ chính xác, các công cụ này đang thay đổi thị trường một cách im lặng - các nhà giao dịch không chỉ giao dịch thông minh hơn, họ đang di chuyển đồng bộ, tạo ra một động lực mới làm tăng cả rủi ro và cơ hội.

Giao dịch AI trong Crypto Giải thích: Cách giao dịch tự trị đang định hình lại thị trường tiền điện tử và sàn giao dịch tiền điện tử
AI Trading đang nhanh chóng biến đổi phong cảnh crypto. Các chiến lược truyền thống đấu tranh để theo kịp sự biến động không ngừng của crypto và cấu trúc thị trường phức tạp, trong khi AI có thể xử lý dữ liệu khổng lồ, tạo ra các chiến lược thích nghi, quản lý rủi ro và thực hiện giao dịch một cách độc lập. Bài viết này hướng dẫn người dùng WEEX qua giao dịch AI là gì, tại sao tiền mã hóa đẩy nhanh sự áp dụng của nó, làm thế nào ngành công nghiệp đang phát triển hướng tới các đại lý tự trị, và tại sao WEEX đang xây dựng hệ sinh thái giao dịch AI thế hệ tiếp theo.

Call to Join AI Wars: WEEX Alpha Awakens - Cuộc thi giao dịch AI toàn cầu với $880,000 Prize Pool
Bây giờ, chúng tôi kêu gọi các nhà giao dịch AI từ khắp nơi trên thế giới tham gia AI Wars: WEEX Alpha Awakens, một cuộc thi thương mại AI toàn cầu với 880.000 USD.

Giao dịch AI trong Crypto Markets: Từ robot giao dịch tự động đến chiến lược thuật toán
Giao dịch do AI thúc đẩy đang chuyển đổi tiền điện tử từ suy đoán bán lẻ sang cạnh tranh ở cấp độ tổ chức, nơi thực thi và quản lý rủi ro quan trọng hơn là hướng đi. Khi giao dịch AI leo thang, rủi ro hệ thống và áp lực quản lý tăng lên, làm cho hiệu suất dài hạn, hệ thống mạnh mẽ và tuân thủ các yếu tố khác biệt quan trọng.

Phân tích cảm xúc AI và biến động tiền mã hóa: Chuyển đổi giá Crypto
Cảm xúc AI đang ngày càng ảnh hưởng đến thị trường tiền điện tử, với những thay đổi trong những kỳ vọng liên quan đến AI chuyển thành sự biến động cho các tài sản kỹ thuật số lớn. Thị trường tiền điện tử có xu hướng mở rộng các câu chuyện AI, cho phép các luồng được thúc đẩy bởi tình cảm vượt quá những yếu tố cơ bản trong ngắn hạn. Hiểu được cảm xúc AI hình thành và phổ biến như thế nào giúp các nhà đầu tư dự đoán tốt hơn chu kỳ rủi ro và định vị cơ hội trên các tài sản kỹ thuật số.

AI Wars: Hướng dẫn tham gia
Trong cuộc so tài đỉnh cao này, các nhà phát triển hàng đầu, chuyên gia định lượng và trader từ khắp thế giới sẽ tung ra các thuật toán của họ trong những trận chiến thị trường thực, cạnh tranh để giành một trong những tổng thưởng lớn nhất trong lịch sử giao dịch crypto bằng AI: 880.000 USD, bao gồm một xe Bentley Bentayga S dành cho nhà vô địch. Hướng dẫn này sẽ đưa bạn qua từng bước bắt buộc từ đăng ký đến thời điểm chính thức bắt đầu cuộc thi.

Banks Week and Crypto Market Volatility: Quyết định lãi suất định hình điều kiện giao dịch trên WEEX
Quyết định lãi suất của các ngân hàng trung ương lớn như Cục Dự trữ Liên bang là những sự kiện kinh tế lớn có ảnh hưởng đến thị trường tài chính toàn cầu, ảnh hưởng trực tiếp đến kỳ vọng thanh khoản thị trường và sự thèm muốn rủi ro. Khi thị trường tiền điện tử tiếp tục phát triển và cấu trúc giao dịch và người tham gia của nó trưởng thành, thị trường tiền điện tử đang dần được kết hợp vào hệ thống định giá kinh tế vĩ mô.

WEEX API Testing: Hướng dẫn chính thức cho AI Trading Hackathon và Crypto Trading API
WEEX API Testing được thiết kế để đảm bảo rằng mọi người tham gia có thể biến logic giao dịch thành thực hiện thực tế. Tất cả các tương tác API diễn ra trên hệ thống giao dịch trực tiếp của WEEX, cho phép người tham gia làm việc trong điều kiện thị trường xác thực thay vì mô phỏng. Với yêu cầu nhập học thấp, nhiệm vụ có thể truy cập cho cả các nhà phát triển có kinh nghiệm và người mới bắt đầu có động lực, trong khi vẫn xác nhận kỹ năng kỹ thuật cần thiết.
Chiến tranh AI: Hướng dẫn tham gia test
Phần 1: Các phương pháp được đề xuất (Cloud Server)
Để có sự ổn định tốt nhất, chúng tôi khuyên bạn nên sử dụng một máy chủ đám mây có IP công cộng tĩnh và hỗ trợ hoạt động không gián đoạn 24/7 như: AWS (Amazon Web Services), Alibaba Cloud, và Tencent Cloud.
Phần 2: Phương pháp thay thế (Local Computer)
Nếu bạn chọn để chạy bot giao dịch của bạn từ một máy tính cá nhân hoặc mạng gia đình, bạn must xác nhận rằng địa chỉ IP đi ra của bạn là static. Một IP thay đổi sẽ dẫn đến các vấn đề kết nối.
Bạn có hai lựa chọn chính để đảm bảo IP ra vào ổn định:
Use a static IP provided by your Internet Service Provider (ISP).Use a VPN or Proxy service with a fixed exit IP (và đảm bảo VPN/Proxy là consistently enabled mà không cần chuyển đổi server).Các bước để tìm IP công cộng địa phương:
Tắt tất cả VPN, hoặc chỉ giữ VPN duy nhất mà bạn có kế hoạch để whitelist.Truy cập whatismyip.com trong trình duyệt của bạn.Trang sẽ hiển thị địa chỉ IPv4 công cộng của bạn.Sao chép IP này và gửi nó vào danh sách trắng.Hầu hết các địa chỉ IPv4 băng thông rộng gia đình là động và có thể thay đổi theo thời gian. Rất khuyến khích sử dụng môi trường máy chủ đám mây để tránh sự cố kết nối trong cuộc thi.
1.3 Thiếu thông tin? Chúng tôi sẽ theo dõiSau khi bạn gửi BUIDL, nhóm WEEX sẽ xem xét ứng dụng của bạn dựa trên các yêu cầu của cuộc thi. Quá trình xem xét thường mất một ngày làm việc.
Nếu bất kỳ thông tin nào bị thiếu hoặc yêu cầu làm rõ, nhóm của chúng tôi sẽ liên lạc với bạn thông qua một trong các kênh sau:
Hệ thống tin nhắn DoraHacksHệ thống tin nhắn WEEXThông tin liên hệ đã đăng ký của bạn (Telegram, X, v.v.)Vui lòng giữ cho thông tin liên lạc của bạn hoạt động và dễ tiếp cận.
Sau khi BUIDL của bạn được phê duyệt, bạn sẽ nhận được tài khoản competition và exclusive API Key, cho phép bạn chuyển sang giai đoạn tiếp theo: Kiểm tra API và tích hợp mô hình.
. Vui lòng đọc kỹ tài liệu API chính thức của WEEX: https://www.weex.com/api-doc/ai/intro
2. Kết nối với một máy chủ đám mây và chạy mã bên dưới. Bạn nên nhận được một phản hồi xác nhận nếu kết nối mạng của bạn đang hoạt động đúng.
curl -s --max-time 10 "https://api-contract.weex.com/capi/v2/market/time"{"epoch":"1765423487.896","iso":"2025-12-11T03:24:47.896Z","timestamp":1765423487896}
2. Kết nối với một máy chủ đám mây và chạy mã bên dưới. Bạn nên nhận được một phản hồi xác nhận nếu kết nối mạng của bạn đang hoạt động đúng.
import time import hmac import hashlib import base64 import requests api_key = "" secret_key = "" access_passphrase = "" def generate_signature_get(secret_key, timestamp, method, request_path, query_string): message = timestamp + method.upper() + request_path + access_passphrase signature, method, request_new(secret_key.encode(), message.encode(), hashlib.sha256).digest() return base64.b64encode(signature).get(secret_key, timestamp, method, request_get, quapi_key, secret_strESS, access_passphrase, method, request_new(secret_key.encode(), hashlib.sha256). "application/json", "locale": "en-US" } url = "https://api-contract.weex.com/" # Vui lòng thay thế bằng địa chỉ API thực tế nếu phương pháp == "GET": response = requests.get(url + request_path+query_string, headers=headers) return response def assets(): request_path = "/capi/v2/account/assets" query_string = "" response = send_request_get(api_key, secret_key, access_passphrase, "GET", request_path, query_string) print(response.status_code) print(response.text) if __name == '____ main assets':

Tại sao WEEX Alpha Awakens là cuộc thi giao dịch AI hay nhất năm 2025? Những điều cần biết
Để tăng tốc các bước đột phá ở giao điểm của AI và crypto, WEEX đang ra mắt Hackathon thương mại AI toàn cầu đầu tiên trên thế giới - AI Wars: Alpha thức dậy. Sự kiện này có một hồ bơi giải thưởng đột phá vượt quá $ 880,000, bao gồm một Bentley Bentayga S cho nhà vô địch cuối cùng.

Chiến tranh AI: WEEX Alpha Awakens | Hướng dẫn quy trình thử nghiệm WEEX Global Hackathon API
AI Wars: WEEX Alpha Awakens đăng ký đã mở. và hướng dẫn này phác thảo cách truy cập vào thử nghiệm API và hoàn thành quá trình thành công.

WEEX Alpha Awakens là gì và làm thế nào để tham gia? Một hướng dẫn đầy đủ
Để tăng tốc các bước đột phá ở giao điểm của AI và crypto, WEEX đang ra mắt Hackathon thương mại AI toàn cầu đầu tiên trên thế giới - AI Wars: Alpha thức dậy.
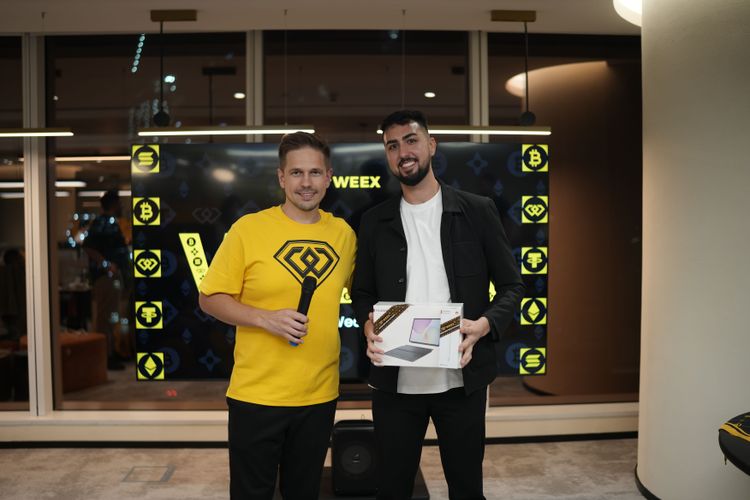

WEEX HODL’em Trading Royale & Dubai Offline Trading Competition Kết thúc thành công
Vào ngày 4 tháng 12 năm 2025, WEEX đã tổ chức Dubai HODL’em Trading Royale đầu tiên và Dubai Offline Trading Competition, mang niềm đam mê của AI WARS vào thế giới thực.

Tham gia AI Wars: WEEX Alpha thức dậy!Global Call cho AI Trading Alpha
AI Wars: WEEX Alpha Awakens là một hackathon thương mại AI toàn cầu ở Dubai, kêu gọi các đội quan sát, các nhà giao dịch thuật toán và các nhà phát triển AI phát hành chiến lược thương mại tiền điện tử AI của họ trên thị trường trực tiếp cho một phần của một hồ bơi giải thưởng 880.000 USD.

WEEX Unveils Trade to Earn: Lên đến 30% trở lại ngay lập tức + $ 2M WXT Buyback
WEEX rất vui khi công bố việc ra mắt chương trình Trade to Earn của chúng tôi, tự động cấp cho bạn giảm giá phí giao dịch lên đến 30%. Tất cả phần thưởng được ghi nhận trực tiếp vào tài khoản spot của bạn trong $WXT - được hỗ trợ bởi kế hoạch mua lại $2.000.000 WXT của chúng tôi, cung cấp giá trị token dài hạn.
WEEXPERIENCE Whales Night: AI Trading, Crypto Community & Crypto Market Insights
Vào ngày 12 tháng 12 năm 2025, WEEX đã tổ chức WEEXPERIENCE Whales Night, một cuộc họp cộng đồng ngoại tuyến được thiết kế để tập hợp các thành viên cộng đồng cryptocurrency địa phương. Sự kiện kết hợp chia sẻ nội dung, trò chơi tương tác và bản trình bày dự án để tạo ra trải nghiệm ngoại tuyến thoải mái nhưng hấp dẫn.
Rủi ro giao dịch AI trong tiền mã hóa: Tại sao các chiến lược giao dịch tiền mã hóa tốt hơn có thể tạo ra tổn thất lớn hơn?
Rủi ro không còn nằm chủ yếu trong việc đưa ra quyết định kém hoặc sai lầm về cảm xúc. Nó ngày càng sống trong cấu trúc thị trường, con đường thực thi, và hành vi tập thể. Hiểu được sự thay đổi này quan trọng hơn là tìm ra chiến lược “tốt hơn” tiếp theo.
Các đại lý AI đang thay thế Nghiên cứu Crypto? Làm thế nào AI tự trị đang định hình lại giao dịch crypto
AI đang chuyển từ việc hỗ trợ các nhà giao dịch sang tự động hóa toàn bộ quá trình nghiên cứu đến thi hành trong thị trường tiền điện tử. Lợi thế đã chuyển từ kiến thức của con người sang đường ống dẫn dữ liệu, tốc độ và các hệ thống AI sẵn sàng để thực hiện, làm cho sự chậm trễ trong tích hợp AI trở thành một nhược điểm cạnh tranh.
Bot giao dịch AI và Giao dịch sao chép: Cách các chiến lược đồng bộ hóa định hình lại sự biến động của thị trường crypto
Các nhà giao dịch crypto bán lẻ từ lâu đã phải đối mặt với những thách thức tương tự: quản lý rủi ro kém, đăng ký muộn, quyết định về cảm xúc và thực thi không nhất quán. Các công cụ giao dịch AI hứa hẹn một giải pháp. Ngày nay, các hệ thống giao dịch sao chép và robot breakout được hỗ trợ bởi AI giúp các nhà giao dịch kích thước vị trí, đặt điểm dừng và hành động nhanh hơn bao giờ hết. Ngoài tốc độ và độ chính xác, các công cụ này đang thay đổi thị trường một cách im lặng - các nhà giao dịch không chỉ giao dịch thông minh hơn, họ đang di chuyển đồng bộ, tạo ra một động lực mới làm tăng cả rủi ro và cơ hội.
Giao dịch AI trong Crypto Giải thích: Cách giao dịch tự trị đang định hình lại thị trường tiền điện tử và sàn giao dịch tiền điện tử
AI Trading đang nhanh chóng biến đổi phong cảnh crypto. Các chiến lược truyền thống đấu tranh để theo kịp sự biến động không ngừng của crypto và cấu trúc thị trường phức tạp, trong khi AI có thể xử lý dữ liệu khổng lồ, tạo ra các chiến lược thích nghi, quản lý rủi ro và thực hiện giao dịch một cách độc lập. Bài viết này hướng dẫn người dùng WEEX qua giao dịch AI là gì, tại sao tiền mã hóa đẩy nhanh sự áp dụng của nó, làm thế nào ngành công nghiệp đang phát triển hướng tới các đại lý tự trị, và tại sao WEEX đang xây dựng hệ sinh thái giao dịch AI thế hệ tiếp theo.
Call to Join AI Wars: WEEX Alpha Awakens - Cuộc thi giao dịch AI toàn cầu với $880,000 Prize Pool
Bây giờ, chúng tôi kêu gọi các nhà giao dịch AI từ khắp nơi trên thế giới tham gia AI Wars: WEEX Alpha Awakens, một cuộc thi thương mại AI toàn cầu với 880.000 USD.
Coin thịnh hành
Tin tức crypto mới nhất
Bộ phận CSKH:@weikecs
Hợp tác kinh doanh:@weikecs
Giao dịch Định lượng & MM:[email protected]
Dịch vụ VIP:[email protected]
